This post shows step-by-step how to create the following 2D mesh:
Personal Blog of Syeilendra Pramuditya
Month: October 2012
In my previous article, I discussed about laminar velocity profile for 2D problem, the numerical solution technique is easily extendible to 3D problem. For example to solve isothermal laminar flow in a square channel problem, as illustrated below:

For this case, linear momentum equation takes the form:
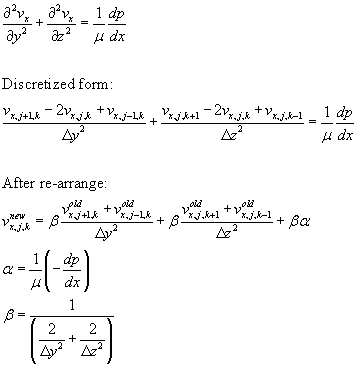
The program is basically very similar to the 2D problem, just in the current case the calculated x-velocity is stored in 2D (or two-index) array. The Fortran code is shown below:
! Laminar velocity profile in square flow channel
! By Syeilendra Pramuditya - https://syeilendrapramuditya.wordpress.com
! October 2012
program main
implicit none
integer j,jmin,jmax,k,kmin,kmax,iter,itermax,conv,prnt
parameter(jmin=0, jmax=40, kmin=0, kmax=40)
real*8 mu,rho,Ly,Lz,uy1,uy2,uz1,uz2,errmax,Re,Dh,uinit,f,mdpdx,
&alpha,uold(jmin:jmax,kmin:kmax),unew(jmin:jmax,kmin:kmax),dy,dz,
&y(jmin:jmax),z(kmin:kmax),dy2,dz2,beta,err
!input
Ly=1.0d-2
Lz=Ly !square channel
uy1=0.0d0
uy2=0.0d0
uz1=0.0d0
uz2=0.0d0
itermax=5000
errmax=1.0d-6
Re=5.0d2
!props
mu=1.0d-3
rho=1.0d3
!calc internal vars
Dh=4.0d0*(Ly*Lz)/(2.0d0*Ly+2.0d0*Lz)
uinit=Re*mu/(rho*Dh)
f=14.0d0/Re !friction factor
mdpdx=(f/Dh)*0.5d0*rho*uinit*uinit ! -dp/dx
alpha=mdpdx/mu
!init all arrays
do j=jmin,jmax
do k=kmin,kmax
uold(j,k)=0.0d0
unew(j,k)=0.0d0
end do
end do
!mesh
dy=Ly/(jmax-jmin)
dy2=dy*dy
y(jmin)=0.0d0
do j=jmin+1,jmax
y(j)=y(j-1)+dy
end do
dz=Lz/(kmax-kmin)
dz2=dz*dz
z(kmin)=0.0d0
do k=kmin+1,kmax
z(k)=z(k-1)+dz
end do
beta=1.0d0/(2.0d0/dy2+2.0d0/dz2)
!init guess of x-velocity
do j=jmin+1,jmax-1
do k=kmin+1,kmax-1
uold(j,k)=uinit
unew(j,k)=uinit
end do
end do
!init boundary condition
do k=kmin,kmax
uold(0,k)=uy1
uold(jmax,k)=uy2
unew(0,k)=uy1
unew(jmax,k)=uy2
end do
do j=jmin,jmax
uold(j,0)=uz1
uold(j,kmax)=uz2
unew(j,0)=uz1
unew(j,kmax)=uz2
end do
!calculate
conv=0
iter=0
do while((conv.eq.0).and.(iter.le.itermax))
conv=1
!calc new u
do j=jmin+1,jmax-1
do k=kmin+1,kmax-1
unew(j,k)=beta*(uold(j+1,k)+uold(j-1,k))/dy2 +
& beta*(uold(j,k+1)+uold(j,k-1))/dz2 + beta*alpha
err=dabs(unew(j,k)-uold(j,k))/unew(j,k)
if(err.ge.errmax) conv=0 !check convergence
end do
end do
!update u
do j=jmin,jmax
do k=kmin,kmax
uold(j,k)=unew(j,k)
end do
end do
iter=iter+1
end do
!output result
prnt=6
write(prnt,*) 'Solution Converged in',iter,'iterations'
write(prnt,*) ' '
write(prnt,*) 'The result has been saved to the following files:'
write(prnt,*) 'xveloc.dat -> calculated x velocity [m/s]'
write(prnt,*) 'ypos.dat -> y coordinate [m]'
write(prnt,*) 'zpos.dat -> z coordinate [m]'
open(10,file="xveloc.dat")
do j=jmin,jmax
write(10,1000) (unew(j,k),k=kmin,kmax)
end do
close(10)
open(10,file="ypos.dat")
do j=jmin,jmax
write(10,1000) y(j)
end do
close(10)
open(10,file="zpos.dat")
do k=kmin,kmax
write(10,1000) z(k)
end do
close(10)
1000 format(1P50E10.3)
stop
end
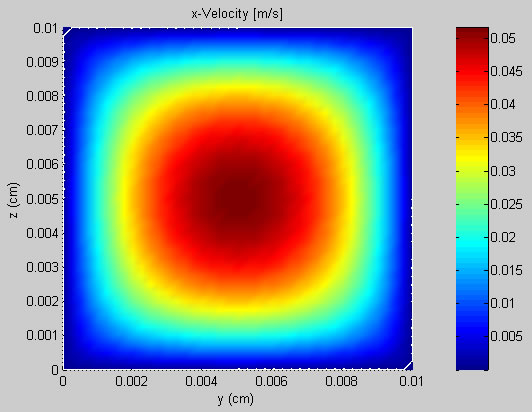
The calculated result can be plotted using the following Matlab m-file:
y=dlmread('ypos.dat',' ');
z=dlmread('zpos.dat',' ');
[Y,Z]=meshgrid(y,z);
VX = dlmread('xveloc.dat',' ');
surf(Y,Z,VX)
shading interp
title('x-Velocity [m/s]')
xlabel('y (cm)'),ylabel('z (cm)'),zlabel('x-Velocity [m/s]')
axis tight;
colorbar;
view(0,90);
And here is the resulting plot:
The real power of numerical solution methods is their ability to approximate the solution of a given mathematical equation for complex geometry. So let’s make this problem a bit more interesting by making the geometry a bit more complex, and we do this by “putting” an immersed rectangular solid object into the flow channel. This is achieved simply by applying a zero-velocity boundary condition at the object’s location. The modified code is available here, and the result is shown below:

—
! Laminar velocity profile between infinite parallel plates
! By Syeilendra Pramuditya - https://syeilendrapramuditya.wordpress.com
! October 2012
program main
implicit none
integer j,jmin,jmax,iter,itermax,conv,prnt
parameter(jmin=0, jmax=10)
real*8 uold(jmin:jmax),unew(jmin:jmax),L,uinit,dy,errmax,
&mu,rho,Re,f,mdpdx,alpha,err,ubot,utop,y(jmin:jmax),
&umath(jmin:jmax)
!input
L=1.0d-2
ubot=0.0d0
utop=0.0d0
itermax=1000
errmax=1.0d-6
Re=5.0d2
!props
mu=1.0d-3
rho=1.0d3
!calc internal vars
uinit=Re*mu/(rho*L) !average x-veloc
f=24.0d0/Re !friction factor
mdpdx=(f/L)*0.5d0*rho*uinit*uinit ! -dp/dx
alpha=0.5d0*mdpdx/mu
!init all arrays
do j=jmin,jmax
uold(j)=0.0d0
unew(j)=0.0d0
end do
!mesh
dy=L/(jmax-jmin)
y(jmin)=0.0d0
do j=jmin+1,jmax
y(j)=y(j-1)+dy
end do
!init guess of x-velocity
do j=jmin+1,jmax-1
uold(j)=uinit
end do
!init boundary condition
uold(jmin)=ubot
uold(jmax)=utop
unew(jmin)=ubot
unew(jmax)=utop
!calculate
conv=0
iter=0
do while((conv.eq.0).and.(iter.le.itermax))
conv=1
!calc new u
do j=jmin+1,jmax-1
unew(j)=0.5d0*(uold(j+1)+uold(j-1))+alpha*dy*dy
err=dabs(unew(j)-uold(j))/unew(j)
if(err.ge.errmax) conv=0 !check convergence
end do
!update u
do j=jmin,jmax
uold(j)=unew(j)
end do
iter=iter+1
end do
!exact solution for static walls
do j=jmin,jmax
umath(j)=0.5d0*(1.0d0/mu)*mdpdx*(L*y(j)-y(j)*y(j))
end do
!result
prnt=6
write(prnt,*) 'Re =',Re
write(prnt,*) 'Solution Converged in',iter,'iterations'
write(prnt,*) ' '
write(prnt,*) ' y [m] u[m/s] umath[m/s]'
do j=jmin,jmax
write(prnt,1000) real(y(j)),real(unew(j)),real(umath(j))
end do
write(prnt,*) ' '
write(prnt,*) 'Result has been saved to fort.10 file'
prnt=10
write(prnt,*) 'Re =',Re
write(prnt,*) 'Solution Converged in',iter,'iterations'
write(prnt,*) ' '
write(prnt,*) ' y [m] u[m/s] umath[m/s]'
do j=jmin,jmax
write(prnt,1000) real(y(j)),real(unew(j)),real(umath(j))
end do
1000 format(1P20E12.3)
stop
end